1 min read
A Slurry of Advanced Techniques for Pumping Micro Silica Beads
Key Takeaways: Fluid Metering’s precision pumps for silica bead slurries handle particle sizes from 3µm to 800µm with low shear, no entrapment, and...
Key Takeaways / Highlights
The Importance of Selecting the Right Pump for Hematology Analyzers
In the design and optimization of hematology analyzers, fluid handling is one of the most critical considerations. These instruments depend on precise, repeatable liquid movements. Whether aspirating whole blood, diluting reagents, transferring waste, or to ensure accurate diagnostic results, selecting the wrong pump can lead to unreliable counts, maintenance issues, and increased operational costs.
For manufacturers and system designer engineers, the challenge is to find a pump technology that delivers exceptional precision, chemical compatibility, and long-term reliability. Among the options available (peristaltic, diaphragm, gear, and syringe pumps) rotating and reciprocating piston pumps consistently stand out as the optimal choice for hematology applications.
The Problem: Precision and Longevity in a Demanding Environment
Hematology analyzers handle small sample volumes and demand extremely accurate dosing, often down to microliter levels, with consistent performance. The pumps used in these systems must also tolerate potentially abrasive fluids and a variety of reagents, all without compromising volumetric accuracy.
Common issues with less suitable pump types include:
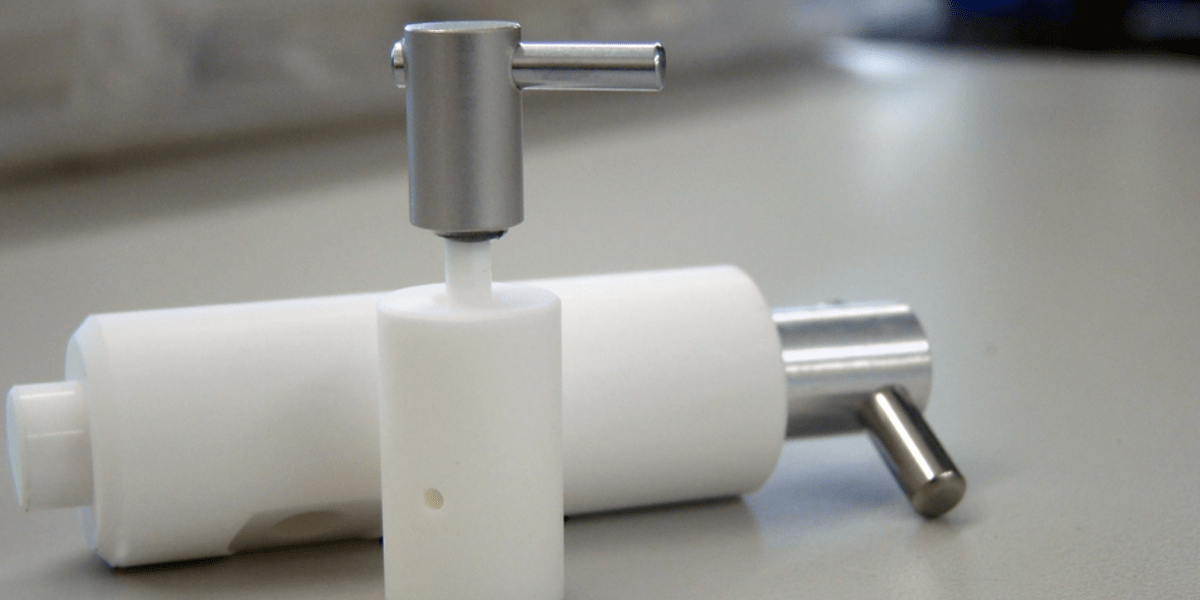
The Solution: Fluid Metering Rotating and Reciprocating Piston Pumps
Rotating and reciprocating piston pumps solve many of the challenges that other pump technologies struggle to overcome. These pumps operate using a piston-driven displacement mechanism that provides highly accurate, repeatable volume control with minimal internal leakage.
Key Advantages:
In a typical 3-part or 5-part differential hematology analyzer, piston pumps can handle a wide range of operations. Such as precise sample aspiration from capillary or venous tubes, accurate mixing and dilution of reagents and samples, timed delivery of lysing or staining agents, and consistent waste disposal with minimized carryover
Unlike peristaltic systems, which can require regular tubing replacement and recalibration, piston pumps offer stable, repeatable performance, reducing downtime and increasing analyzer throughput.
Conclusion: A Smarter Investment for High-Performance Diagnostics
In the evolving landscape of in-vitro diagnostics, analyzer reliability and accuracy are more important than ever. Fluid Metering pumps provide the performance, durability, and fluid control precision required by modern hematology systems. Whether you’re designing a new analyzer or optimizing an existing platform, Fluid Metering pump technologies offer a smart, scalable, and long-term solution, ensuring every drop counts.
*Please contact our technical sales team to discuss your unique requirements.

1 min read
Key Takeaways: Fluid Metering’s precision pumps for silica bead slurries handle particle sizes from 3µm to 800µm with low shear, no entrapment, and...

1 min read
Key Takeaways: For precision piston pumps vs. peristaltic pumps, Fluid Metering’s valveless designs deliver superior accuracy, high-pressure...
Key Takeaways: Fluid Metering’s low-maintenance microfluidic pumps for lab automation deliver long-term precision with minimal wear, thanks to a...